Network Load Balancing: A Comprehensive Guide
Welcome to IT4U, In today’s fast-paced IT world, ensuring high availability and scalability for applications and services is paramount. Network Load Balancing (NLB) is a robust solution that empowers businesses to distribute workloads effectively across multiple servers, ensuring seamless performance and reliability. This blog post delves deep into the intricacies of NLB, its advantages, and its configuration, as covered in my YouTube video, “MCSA Full Course Day 18 – Network Load Balancing.
What is Network Load Balancing?
Network Load Balancing is a technique used to distribute network traffic across multiple servers, ensuring no single server becomes overwhelmed with requests. It is a critical component in modern IT infrastructure, particularly for applications requiring high availability and consistent performance.
For instance, consider an e-commerce website experiencing a surge in traffic during a sale. Without load balancing, a single server may crash due to excessive demand. NLB ensures that incoming traffic is evenly distributed among multiple servers, maintaining smooth operation.
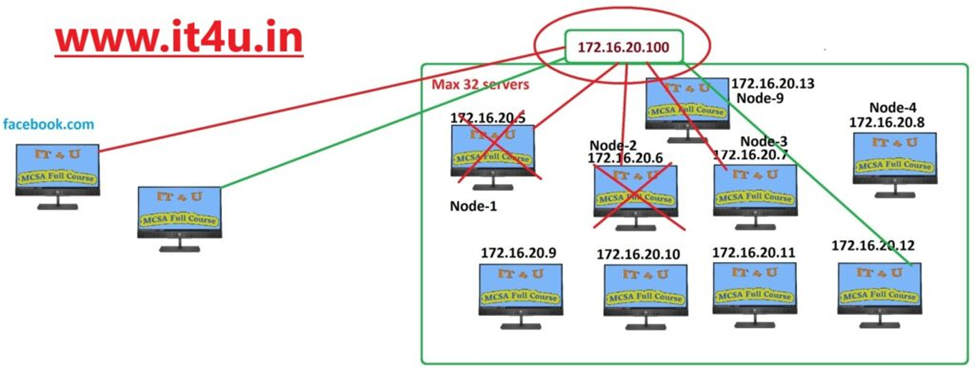
What is a Cluster in Network Load Balancing?

A cluster is a group of servers working together to provide a unified service. In the context of NLB, a cluster consists of multiple nodes (servers) that share the load. The requirements for setting up an NLB cluster include:
- Servers with identical configurations: All nodes in the cluster should have similar hardware and software setups.
- Static IP addresses: Dynamic IPs can disrupt communication within the cluster.
- Network adapters: Each server must have at least one network adapter configured for NLB.
Advantages of Network Load Balancing
NLB offers two primary advantages:
1. High Availability
NLB ensures continuous service availability even if one or more servers in the cluster fail. This fault tolerance is vital for mission-critical applications.
2. Scalability
As traffic increases, you can add more servers to the cluster, ensuring the system scales seamlessly to meet demand.
How Does Network Load Balancing Work?
How Does Network Load Balancing Work
NLB functions by distributing incoming traffic based on several factors:
- Ports: Specific ports can be targeted for load balancing, ensuring only the necessary traffic is managed.
- Priorities: Each server in the cluster is assigned a priority, determining the order in which servers handle traffic.
- Affinity: This determines how client requests are distributed. There are three types:
- None: Any server can handle requests.
- Single: Requests from the same client are sent to the same server.
- Class C: Traffic from the same subnet is directed to the same server.
Cluster Operation Modes
NLB supports three operation modes:
1. Unicast Mode
In this mode, the MAC address of all nodes is replaced with a single shared MAC address. While simple to configure, it can cause network flooding.
2. Multicast Mode
Here, the cluster uses a multicast MAC address, allowing communication between nodes. It avoids flooding but requires additional network configuration.
3. IGMP Multicast Mode
This is an enhancement of multicast mode. It uses Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) to restrict traffic to specific ports, reducing unnecessary network load.
Configuring Network Load Balancing
Setting up an NLB cluster involves several steps:
- Install NLB feature: Add the NLB feature on each server through the Server Manager.
- Create a new cluster: Use the NLB Manager tool to create a cluster and add nodes.
- Configure cluster settings: Specify the IP address, operation mode, and affinity settings.
- Test the configuration: Ensure traffic is distributed as expected and the cluster is functioning correctly.
For a detailed step-by-step guide, check out the video below:
Watch the full video here
MCSA Full Course Day 18 – Network Load Balancing
Conclusion
Network Load Balancing is a vital tool for ensuring the high availability and scalability of your IT services. By distributing traffic across multiple servers, it minimizes downtime, optimizes resource utilization, and enhances user experience. Whether you’re managing an e-commerce platform or a corporate application, NLB is an essential component of a robust IT infrastructure.
For a more in-depth explanation and practical demonstration, don’t forget to watch the embedded YouTube video. If you face any issues, feel free to leave a comment below. Stay tuned for more IT insights on it4u.in!