Active Directory Sites and Services (Part 1)
Introduction
Active Directory Sites and Services is a powerful Microsoft console that allows administrators to define site topology, control replication, and manage authentication traffic across multiple domain controllers. Understanding this concept is essential when working in organizations that operate from multiple offices or geographic locations.
This is Part 1, where we will focus on theory, concepts, and structure. In Part 2, we will perform the practical setup and configuration.
What is Active Directory Sites and Services?
Active Directory Sites and Services is a Microsoft Management Console (MMC) used to:
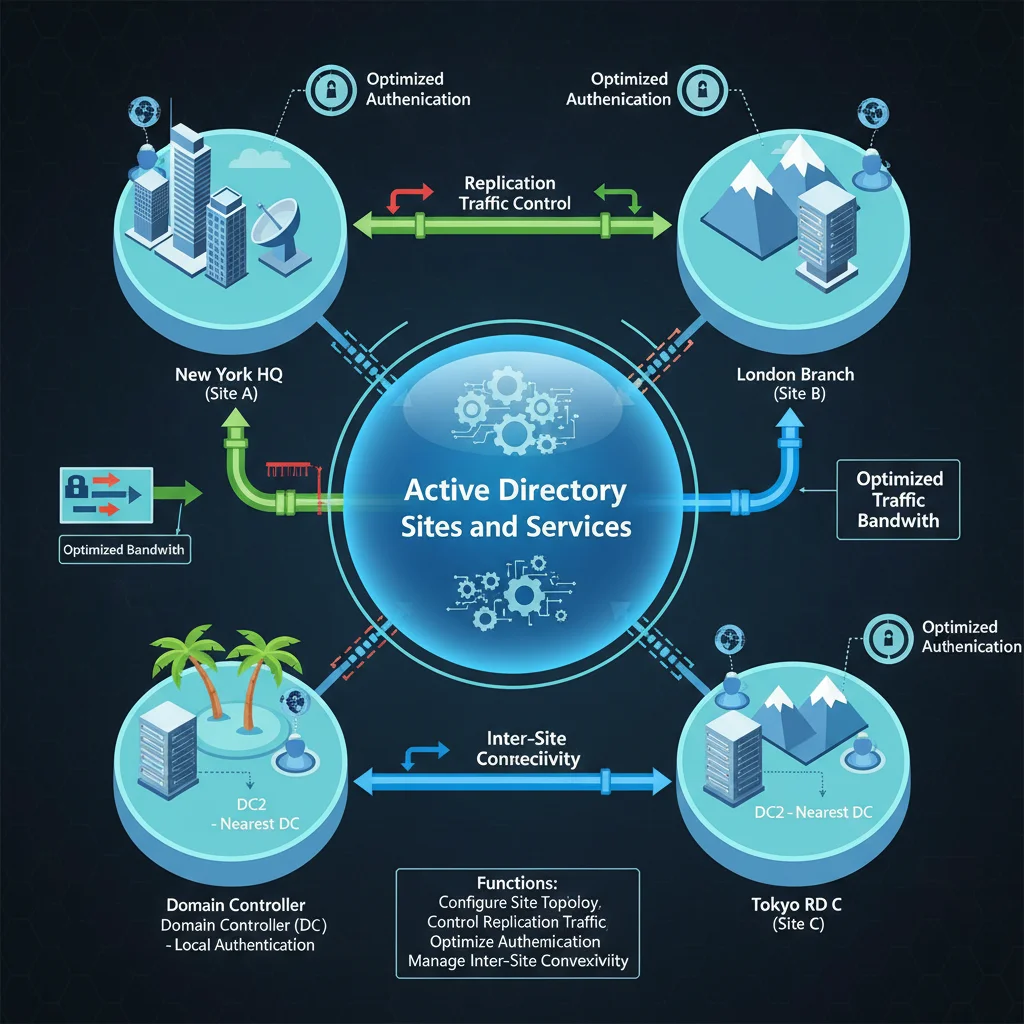
- Configure and manage site topology.
- Control replication traffic between Domain Controllers.
- Optimize authentication traffic for users.
- Manage inter-site connectivity.
👉 In simple terms:
- Sites represent physical network locations (like offices in different cities).
- Services handle replication and authentication processes between those sites.
This ensures users always connect to the nearest Domain Controller, improving login times and network performance.
Key Components of AD Sites and Services
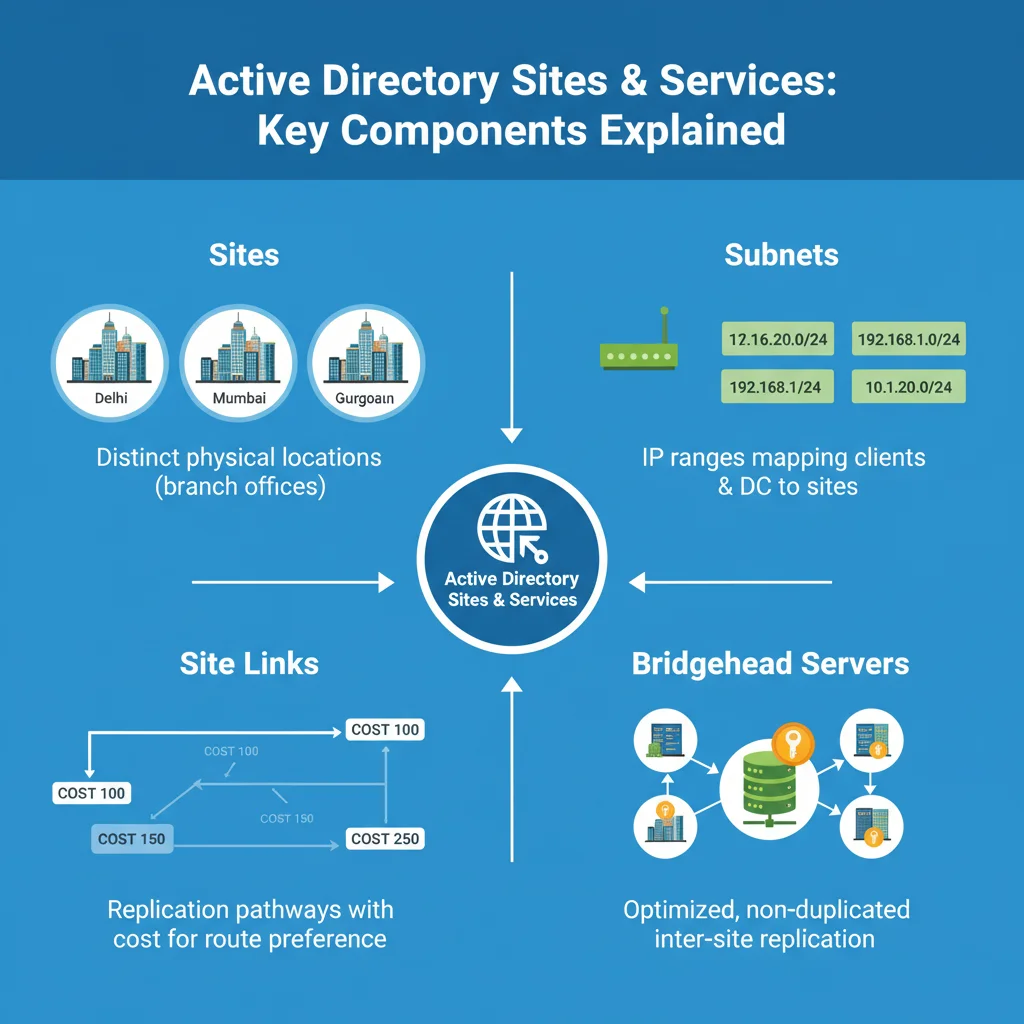
1. Sites
- Represent physical locations in your network (Delhi, Mumbai, Gurgaon, etc.).
- Useful for organizations with branch offices across different regions.
2. Subnets
- Define the IP address ranges associated with each site.
- Help AD understand which Domain Controller should serve which location.
Example:
- Delhi office:
172.16.20.0/24 - Mumbai office:
192.168.1.0/24 - Gurgaon office:
10.1.20.0/24
When a Domain Controller or client uses an IP from one of these subnets, AD maps it to the correct site.
3. Site Links
- Define replication paths and schedules between sites.
- Example: A site link from Delhi to Mumbai, and another from Mumbai to Gurgaon.
- Also include cost values (lower cost = preferred replication path).
4. Bridgehead Servers
- Handle inter-site replication.
- Ensure replication traffic is optimized and not duplicated.
- Act as a “gatekeeper” for replication across sites.
Intra-Site vs Inter-Site Replication
Replication ensures that all Domain Controllers in the forest have consistent information.
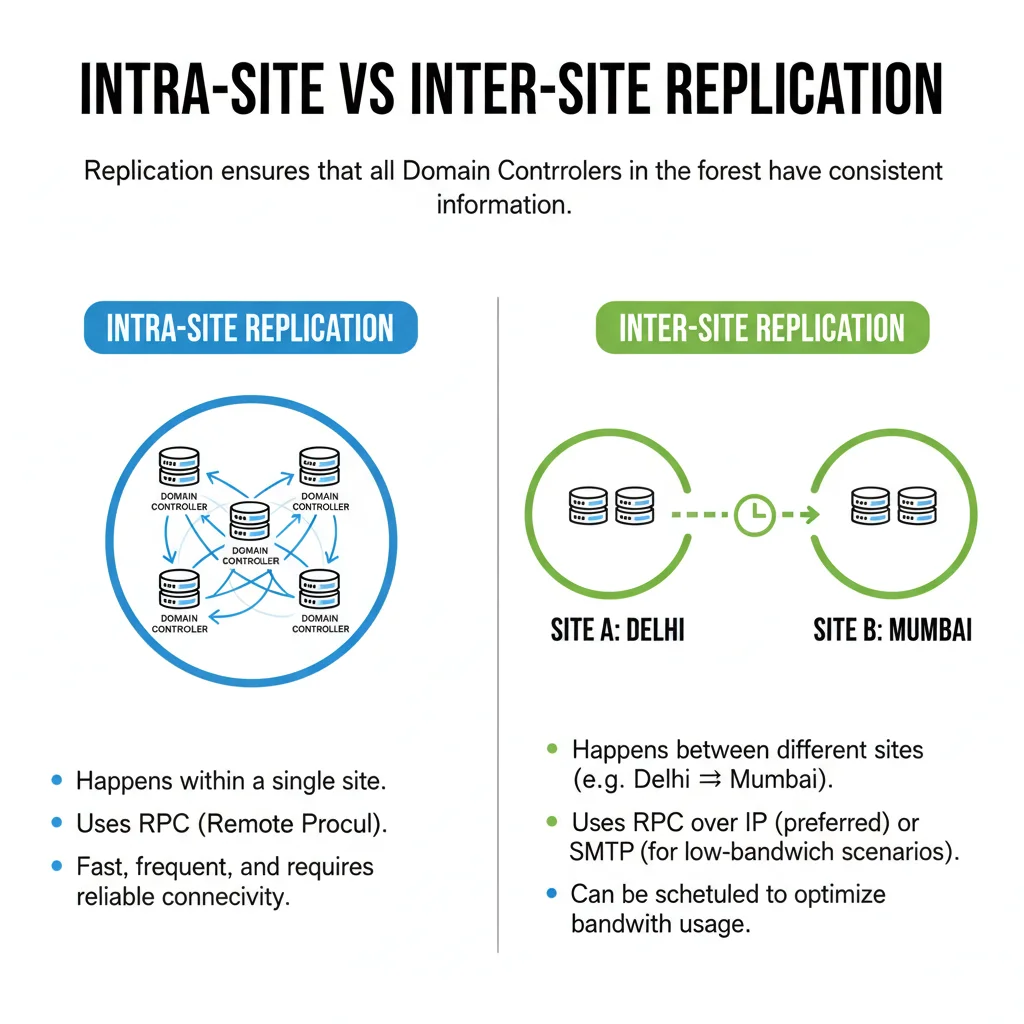
- Intra-Site Replication
- Happens within a single site.
- Uses RPC (Remote Procedure Call).
- Fast, frequent, and requires reliable connectivity.
- Inter-Site Replication
- Happens between different sites (e.g., Delhi ↔ Mumbai).
- Uses RPC over IP (preferred) or SMTP (for low-bandwidth scenarios).
- Can be scheduled to optimize bandwidth usage.
Why Are AD Sites and Services Important?
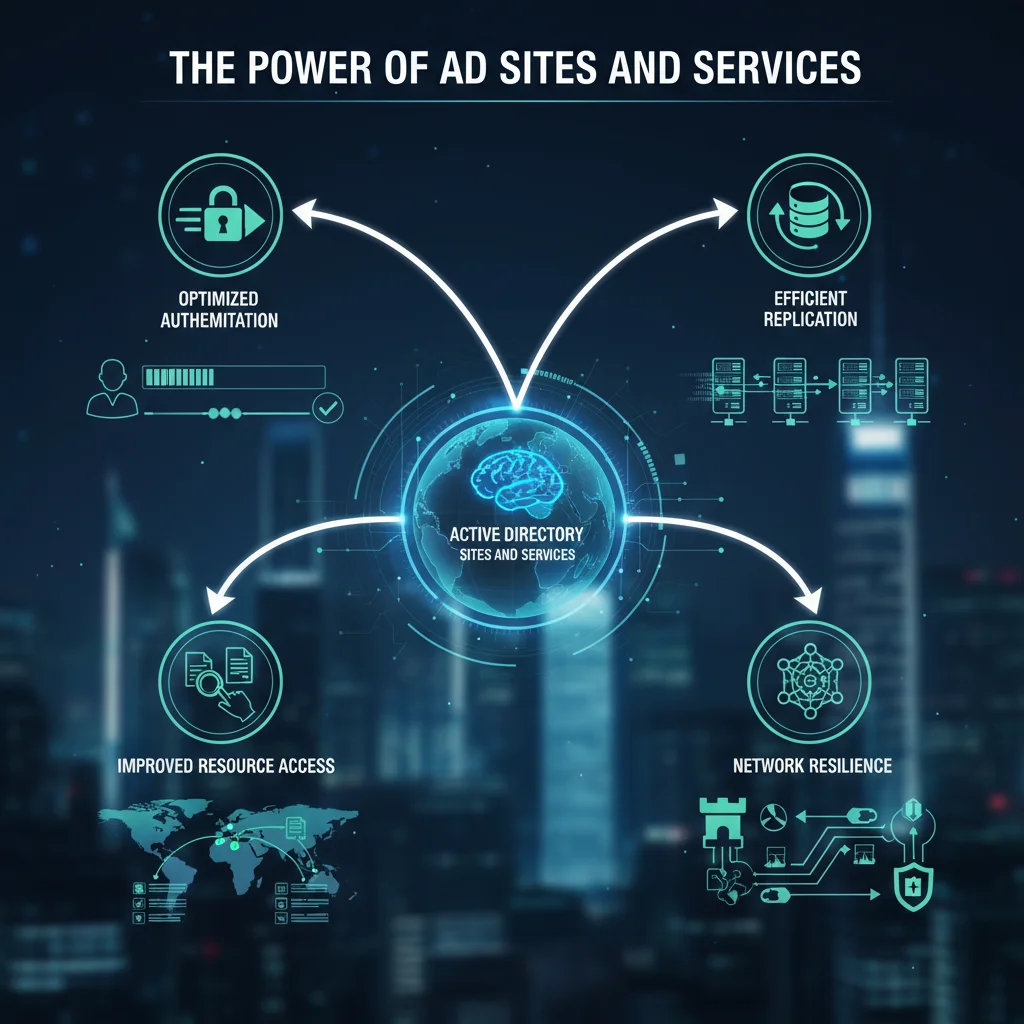
- Optimized Authentication
- Users authenticate with the nearest Domain Controller, reducing login times and network delays.
- Efficient Replication
- Prevents unnecessary data transfer.
- Ensures important changes replicate only when needed.
- Improved Resource Access
- Users connect to the closest servers, improving application performance.
- Network Resilience
- Provides redundancy and prevents excessive inter-site traffic.
- Maintains stability even during connectivity issues.
How Does AD Sites and Services Work?
- AD uses the Knowledge Consistency Checker (KCC) to automatically generate intra-site and inter-site replication links.
- Administrators can manually create or adjust site links, subnets, and replication schedules for better control.
- Cost-based routing ensures that replication follows the most efficient path between sites.
Example Scenario
Imagine your company has offices in:
- Delhi (Head Office)
- Mumbai (Branch Office)
- Gurgaon (Branch Office)
Without AD Sites and Services:
- All Domain Controllers replicate without structure, causing unnecessary traffic.
- Users may authenticate with a DC from another city, increasing login times.
With AD Sites and Services:
- Each office has its own subnet and site.
- Replication follows site links with defined schedules.
- Users always authenticate with the nearest DC, saving bandwidth and time.
FAQ – Active Directory Sites and Services (Part 1)
Q1: What is the purpose of AD Sites and Services?
It helps administrators control replication traffic and ensure users authenticate with the nearest Domain Controller.
Q2: What are the key components of Sites and Services?
Sites, Subnets, Site Links, and Bridgehead Servers.
Q3: What is the difference between intra-site and inter-site replication?
Intra-site happens within a single site (fast, frequent), while inter-site happens between different sites (scheduled, bandwidth-optimized).
Q4: How does a client know which Domain Controller to use?
AD uses the client’s IP address and subnet mapping to direct it to the correct site/DC.
Q5: Why do we assign cost values to site links?
Cost determines replication preference. Lower cost = preferred path.
Q6: Can SMTP be used for replication?
Yes, SMTP can be used for inter-site replication in low-bandwidth scenarios, but RPC over IP is recommended.
Q7: What tool is used to manage Sites and Services?
The Active Directory Sites and Services MMC console in Windows Server.
Conclusion
Active Directory Sites and Services is the backbone of managing a distributed AD environment. By creating sites, subnets, and site links, administrators can optimize replication, improve login times, and ensure efficient use of network resources.
This was Part 1 (Concepts) of AD Sites and Services. In the next blog (Part 2), we will perform the practical configuration step by step.
💡 What do you think about AD Sites and Services? Have you configured it in your environment?
Share your experience in the comments and don’t forget to subscribe to IT4U for more tutorials in this MCSA Full Course.









Hello Sir please share active directory sites and services part-2 blog