Active Directory Sites and Services (Part 2)
Introduction
In Day 41 (Part 1) of this series, we covered the theory of Active Directory Sites and Services—its purpose, components, and why it is critical for organizations with multiple locations.
Now, in Day 42 (Part 2), we move on to the practical configuration. In this session, we will configure different networks, routers, and additional domain controllers (ADC) across multiple sites (Delhi, Mumbai, and Gurgaon). By the end of this tutorial, you will clearly understand how sites communicate through a router server and how replication works in a distributed AD environment.
Practical Lab Setup
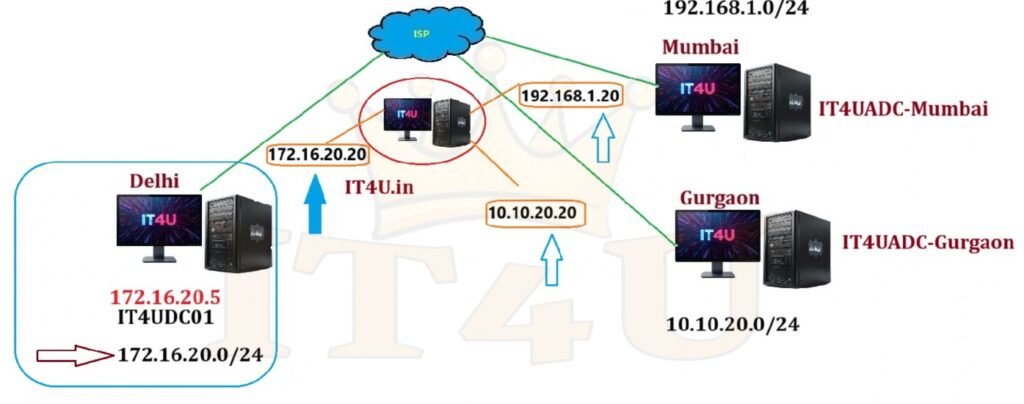
1. Lab Environment
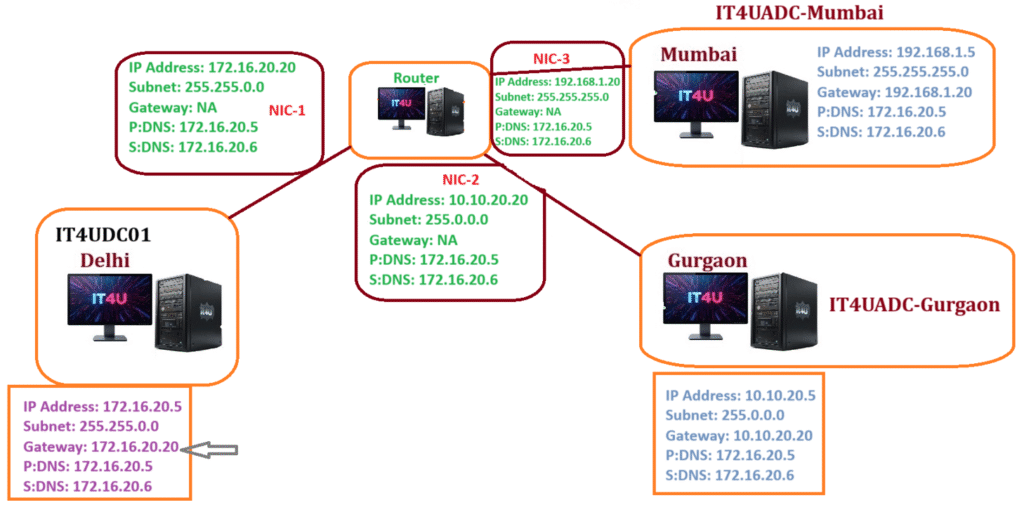
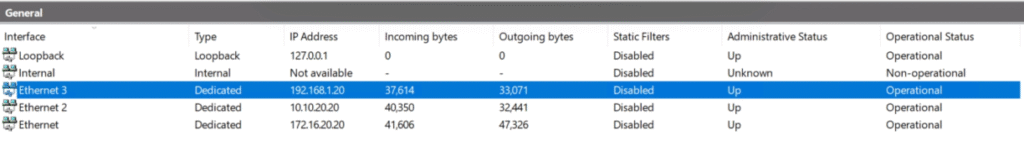
We created a router server with three network adapters:
- NIC 1 – Connected to the Delhi site
- NIC 2 – Connected to the Gurgaon site
- NIC 3 – Connected to the Mumbai site
This router acts as a bridge to ensure communication between all sites.
👉 Note: In a real company environment, you don’t normally need this setup if you already have public IPs and firewalls connecting your locations. This lab simulation is only for practice.
2. Assigning IP Addresses to Router NICs
Each NIC was given a unique IP address for its site:
- NIC 1 (Delhi):
172.16.20.20 - NIC 2 (Gurgaon):
10.10.20.20 - NIC 3 (Mumbai):
192.168.1.20
⚡ DNS servers used:
- Primary DNS →
172.16.20.5 - Secondary DNS →
172.16.20.6
👉 Gateways are not required for the router NICs since the server itself acts as the router.
3. Configuring the Router Server
To enable routing between sites:
- Open Server Manager → Add Roles and Features.
- Install the Remote Access role.
- Under role services, select Routing.
- Open Routing and Remote Access (RRAS) from the Tools menu.
- Right-click the server → Configure and Enable Routing and Remote Access.
- Choose Custom Configuration → Enable LAN Routing.
- Start the service.
At this point, the router server can now handle communication between all three sites.
4. Configuring Site Subnets
In Active Directory Sites and Services, we define subnets for each location:
- Delhi:
172.16.20.0/24 - Gurgaon:
10.10.20.0/24 - Mumbai:
192.168.1.0/24
Each subnet is then linked to its corresponding site so that any server using that subnet is automatically placed in the correct site.
5. Promoting ADCs in Gurgaon and Mumbai
Now, let’s configure additional domain controllers (ADC) in each branch site.
Steps:
- On the Gurgaon server:
- Assign IP:
10.10.20.5 - Gateway:
10.10.20.20(Router NIC for Gurgaon) - DNS:
172.16.20.5&172.16.20.6 - Add the Active Directory Domain Services role.
- Promote the server as an Additional Domain Controller for
it4u.in.
- Assign IP:
- On the Mumbai server:
- Assign IP:
192.168.1.5 - Gateway:
192.168.1.20(Router NIC for Mumbai) - DNS:
172.16.20.5&172.16.20.6 - Add the Active Directory Domain Services role.
- Promote the server as an ADC for
it4u.in.
- Assign IP:
Verification and Replication
Once both Additional Domain Controllers (ADCs) were promoted in Gurgaon and Mumbai, here’s how we verified everything:
1. Checking Site Placement
- Open Active Directory Sites and Services.
- Expand each site:
- Delhi Site → Contains DC01 and existing ADCs.
- Gurgaon Site → Shows the newly promoted
IT4U-ADC-Gurgaon. - Mumbai Site → Shows the newly promoted
IT4U-ADC-Mumbai.
- Because we pre-defined subnets, each ADC automatically appeared in the correct site container.
👉 If a server does not show up in the expected site, double-check its IP address assignment and subnet configuration.
2. Replication Status
- Replication between sites was verified under NTDS Settings in AD Sites and Services.
- Right-click the connection object → Replicate Now to force replication.
- By default, intra-site replication (within the same site) happens frequently and uses RPC, while inter-site replication (between sites) follows a scheduled interval and may use RPC or SMTP depending on configuration.
3. Manual Replication with Command Line
If replication does not happen immediately, you can use:
repadmin /syncall /AdeP/A→ Sync all partitions./d→ Identify servers by distinguished name in output./e→ Enterprise-wide replication (all sites)./P→ Push changes outward.
This ensures that all domain controllers across all sites replicate without waiting for the schedule.
4. Testing in Real Environment
In a real company environment, verification usually includes:
- Event Viewer Logs → Check
Directory ServiceandFile Replication Servicelogs for replication errors. - Dcdiag Tool → Run
dcdiag /test:replicationsto confirm health. - Nslookup → Ensure each ADC resolves properly in DNS.
- User Logins → Test authentication from client machines in Gurgaon and Mumbai. Clients should authenticate with the nearest DC to reduce login delays.
5. Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Issue: ADC not showing under site.
- ✅ Fix: Verify subnet assignment and server’s IP address.
- Issue: Replication is failing.
- ✅ Fix: Check firewalls, routing, and DNS resolution between sites.
- Issue: Clients authenticating to remote DCs.
- ✅ Fix: Ensure site and subnet mapping is correct.
Key Learnings from This Practical
- Router Role Simulation – Essential for labs without public IPs.
- Subnet Mapping – Automatically places servers in the correct site.
- Replication Across Sites – Works seamlessly when DNS and routing are configured correctly.
- ADCs in Different Locations – Ensure redundancy and local authentication.
- Troubleshooting Tip – Always verify DNS and IP assignments before checking replication issues.
FAQ – Active Directory Sites and Services (Part 2)
Q1: Why do we need a router in this lab setup?
Because we don’t have public IPs. In real environments, firewalls/ISPs handle site connectivity.
Q2: How are subnets linked to sites?
Each site is assigned an IP range (subnet). Any server with an IP from that range is automatically placed in the site.
Q3: What happens if replication doesn’t work?
Check DNS settings, verify gateways, and run the command repadmin /syncall /AdeP.
Q4: Why use IFM (Install from Media)?
IFM reduces bandwidth usage by creating ADCs from pre-prepared media instead of replicating over WAN.
Q5: Can third-party tools replace AD Sites and Services?
Yes, some companies use third-party management solutions for large-scale environments, but AD Sites and Services remains the core tool.
Q6: Do we always need Sites and Services?
Not in every company. Small organizations with a single office may not use it, but it’s essential for multi-location enterprises.
Conclusion
With this practical session, we’ve successfully set up Active Directory Sites and Services across Delhi, Mumbai, and Gurgaon using a router server and subnet mapping. Each site now has its own ADC, ensuring optimized authentication, replication, and redundancy.
💡 Question for you: Have you ever worked with AD Sites and Services in a real company setup? Share your experience in the comments below!









Add comment