Active Directory Users, Groups and OU Windows Server 2019
Understanding Users, Groups, and Organizational Units (OUs) in Windows Server 2019
Windows Server 2019, as the backbone of many enterprise IT infrastructures, offers robust tools for managing user accounts, groups, and organizational units (OUs) in Active Directory (AD). These components are fundamental to managing and securing a network of computers and users, especially in larger or more complex environments.
In this post, we’ll explore the core concepts of Users, Groups, and Organizational Units (OUs) in Windows Server 2019, how they work together to streamline network administration, and best practices for using these features effectively.
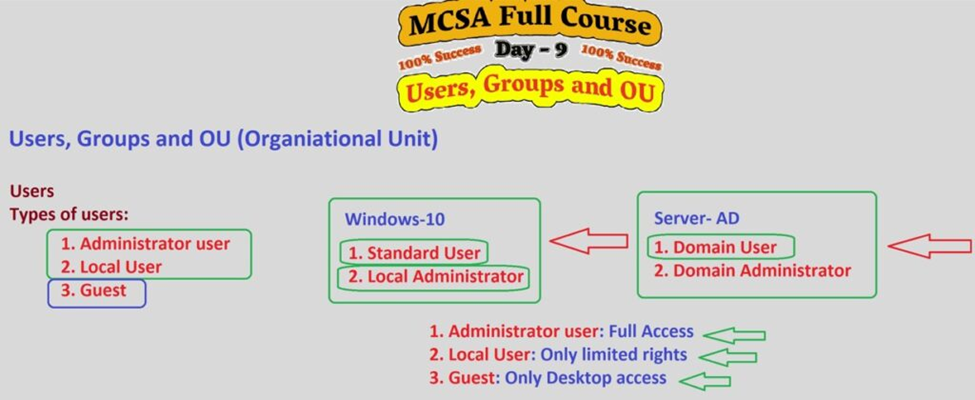
1. Understanding Users in Windows Server 2019
In Active Directory, users are individuals who need to access resources in a network environment. A user account in Windows Server 2019 is an object within Active Directory that represents an individual (or a service) requiring access to the domain.
Key Features of User Accounts:
- Attributes: Each user account has a variety of attributes, such as username, password, and contact information (e.g., email address, phone number).
- Login Credentials: User accounts authenticate against the domain, providing access to resources such as files, printers, and applications based on permissions set by an administrator.
- Security: Administrators can assign security settings, such as password policies, account lockout policies, and group memberships, to enhance the security of user accounts.
Creating and Managing User Accounts:
In Windows Server 2019, you can create and manage user accounts using the Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) tool.
- To create a new user:
- Open Active Directory Users and Computers.
- Navigate to the appropriate Organizational Unit (OU) or container.
- Right-click, choose New, and then select User.
- Enter the user’s details (name, username, etc.) and set the password.
- Assign the user to specific groups or set additional properties like email, contact info, or home directory.
- User Permissions: Once the user is created, you can control what they can access by setting permissions on shared resources or assigning them to groups.
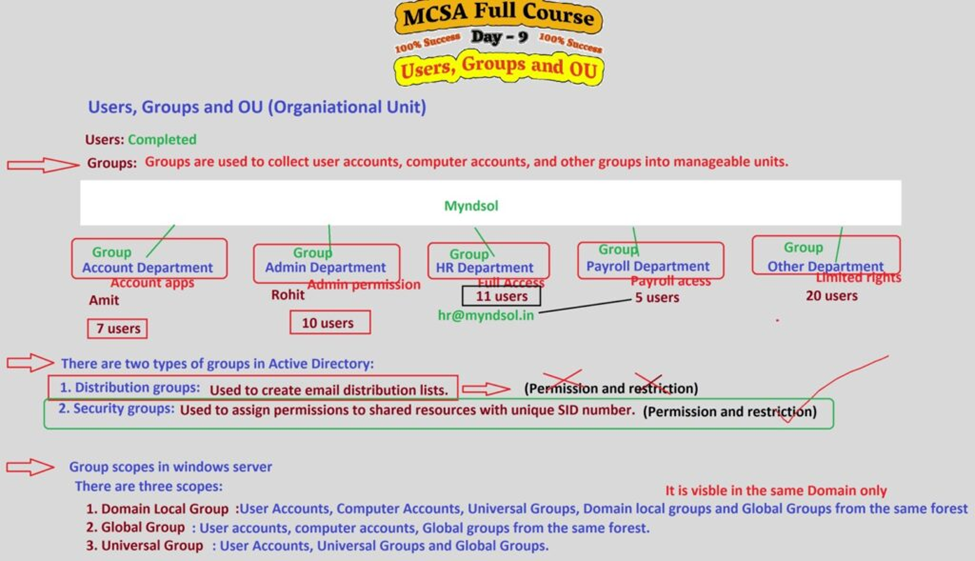
2. Understanding Groups in Windows Server 2019
In Windows Server 2019, groups are collections of users (or other groups) that can be managed as a single unit. They simplify the process of assigning permissions to multiple users simultaneously. Instead of assigning permissions to individual users, you can assign them to groups, and all members of that group automatically inherit those permissions.
Types of Groups:
Windows Server 2019 supports two main types of groups:
- Security Groups: These groups are used to assign permissions to shared resources. When a user is part of a security group, they can access resources that the group has permissions for.
- Distribution Groups: These groups are used for email distribution lists and don’t have permissions associated with them.
Group Scope:
Groups in Windows Server 2019 can have one of three scopes, determining where they can be used:
- Domain Local Group: Primarily used within a single domain. These groups are typically used to assign permissions to resources within the same domain.
- Global Group: Can include members from the same domain but can be assigned permissions to resources in any domain within the forest.
- Universal Group: Can include members from multiple domains in a forest and can be used to assign permissions across the entire forest.
Best Practices for Group Management:
- Least Privilege: Use the principle of least privilege to grant only the minimum necessary permissions. Groups allow you to assign permissions efficiently and with less risk of granting excessive access.
- Group Nesting: You can nest groups within other groups. For example, you can place a Global Group inside a Domain Local Group to assign permissions to a broader audience.
Managing Groups:
You can manage groups in Windows Server 2019 using the Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) tool, where you can create, modify, and delete groups, as well as add or remove group members.
3. Organizational Units (OUs) in Windows Server 2019
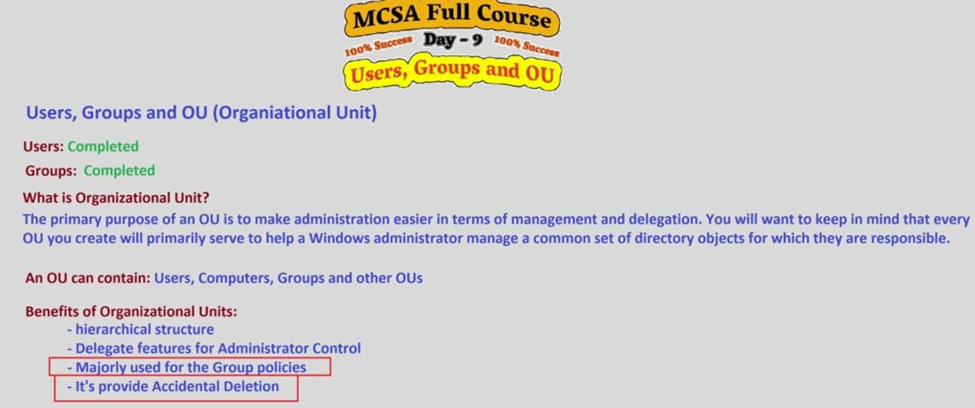
An Organizational Unit (OU) is a container within Active Directory that is used to organize and manage users, groups, computers, and other resources. OUs provide a hierarchical structure, allowing administrators to delegate administrative tasks and apply Group Policy settings to a specific subset of users or resources.
Key Features of OUs:
- Hierarchy: OUs can be nested within each other, allowing for a flexible structure that mimics your organizational structure (e.g., departments, geographic locations).
- Delegation: Administrators can delegate specific administrative permissions for an OU. For example, a manager in a specific department can be given control over only the users in their department’s OU without affecting the entire domain.
- Group Policies: You can link Group Policy Objects (GPOs) to OUs, applying specific policies to the users or computers within the OU. This is a powerful way to enforce security settings or other configurations across a subset of your environment.
Creating and Managing OUs:
To create an OU in Windows Server 2019:
- Open Active Directory Users and Computers.
- In the ADUC console, right-click on the domain or a parent OU.
- Select New > Organizational Unit.
- Give the OU a name and configure it as needed.
After creating the OU, you can move users, groups, or other objects into the OU, as well as apply GPOs to control settings.
Best Practices for Organizing Users, Groups, and OUs
To effectively manage users, groups, and organizational units in Windows Server 2019, it’s important to follow best practices that ensure scalability, security, and ease of administration.
- Plan Your OU Structure: Create a logical structure that reflects your organizational hierarchy. This can include OUs for departments (e.g., HR, IT, Sales) or locations (e.g., New York Office, London Office).
- Use Group Naming Conventions: Maintain consistent naming conventions for groups and OUs to make it easier to manage and troubleshoot. For example, prefix group names with “HR-“ for HR-related groups or “NY-“ for New York office groups.
- Apply Group Policies Strategically: Link GPOs to OUs to enforce settings for users and computers within those OUs. For example, you can enforce password policies or desktop settings for the Sales OU without affecting other departments.
- Regular Audits and Reviews: Regularly review user and group memberships to ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive resources. Remove inactive users and update group memberships as needed.
- Delegate Control: Use delegation to grant specific administrative permissions for OUs. This reduces the administrative burden on domain admins and helps distribute management responsibilities.
Conclusion
Users, Groups, and Organizational Units are fundamental components of Active Directory in Windows Server 2019. Understanding how to manage and organize these objects efficiently can significantly improve the security, scalability, and administration of your network. By leveraging the powerful features of AD, such as group memberships, OUs, and GPOs, you can streamline your server management tasks and maintain a secure and well-organized IT environment.
By following best practices and utilizing the management tools available in Windows Server 2019, administrators can ensure a smooth and efficient Active Directory deployment, making the network more secure and easier to maintain.
Need more tips on Active Directory management? Stay tuned for more guides and tutorials to help you optimize your server environments.
For a step-by-step installation guide, be sure to visit my video where I explained each step in detail. If you’re still facing any issues, feel free to comment below, and I’ll be happy to help you resolve them.